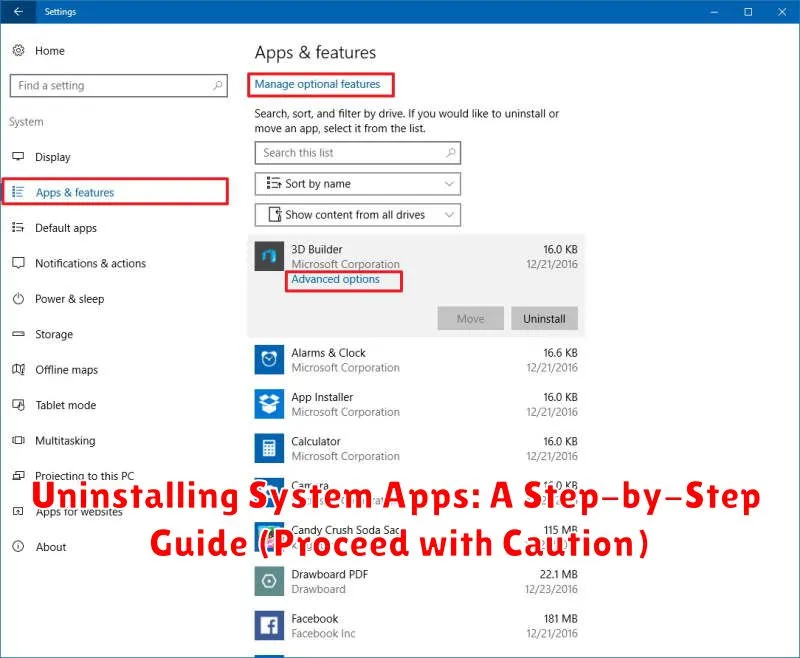
System apps, those pre-installed applications residing on your device, can sometimes feel like unwelcome guests. They might consume valuable storage space, drain battery life, or simply clutter your interface. While some system apps are essential for the core functionality of your device, others can be safely removed. This step-by-step guide will demonstrate how to uninstall system apps on various platforms, including Android and iOS. However, we must strongly emphasize the importance of proceeding with caution. Uninstalling the wrong system app can lead to instability, data loss, or even render your device unusable. Therefore, carefully consider the potential consequences before proceeding with any system app removal.
Before you embark on the journey of uninstalling system apps, it’s crucial to understand the risks involved. While this guide provides a detailed walkthrough, it’s your responsibility to identify which system apps are safe to remove. Back up your device before making any changes, as this will allow you to restore your system to a working state if something goes wrong. Furthermore, this guide differentiates between disabling and uninstalling system apps, highlighting the implications of each action. This comprehensive guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and steps necessary to safely and effectively manage your system applications, allowing you to reclaim storage, improve performance, and personalize your device experience.
Understanding System Apps and Their Importance
System apps, also known as pre-installed apps, are applications included on your device by the manufacturer or operating system provider. They form the core functionality of your device and often handle essential tasks.
These apps range from basic utilities like the phone dialer and messaging app to more complex services managing background processes. They are typically integrated tightly with the operating system, allowing for efficient resource management and optimized performance.
Importance of System Apps:
- Core Functionality: System apps provide essential functionalities like making calls, sending messages, managing settings, and accessing the internet.
- Operating System Stability: Many system apps are crucial for maintaining the operating system’s stability and security.
- Hardware Integration: These apps often manage and interact directly with the device’s hardware, ensuring proper functionality.
- Pre-optimized Performance: Being pre-installed, these apps are generally optimized for the specific device, resulting in smoother performance and lower battery consumption.
Risks and Benefits of Uninstalling System Apps
Uninstalling system apps can offer both advantages and disadvantages. It’s crucial to weigh these carefully before proceeding.
Potential Benefits
Removing unused system apps can free up storage space and potentially improve device performance. It can also reduce clutter in your app drawer and simplify your user experience. Some system apps might consume background resources, and uninstalling them could improve battery life.
Potential Risks
Uninstalling essential system apps can lead to system instability, app malfunctions, or even render your device unusable. Data loss is another potential risk. Critical system features may be disabled, impacting functionality. Certain apps are interconnected, and removing one might affect others. Security vulnerabilities can arise if crucial security-related apps are uninstalled.
Proceed with extreme caution. Thoroughly research any system app before uninstalling it to understand its function and potential impact.
Identifying System Apps on Your Device
Before attempting to uninstall any system apps, it’s crucial to correctly identify them. Misidentifying an app can lead to unintended consequences. There are a few key indicators that can help you distinguish system apps from user-installed apps.
App Location: System apps are typically pre-installed and reside in a system directory. While the exact location may vary depending on your device’s operating system, they are generally found within protected folders inaccessible without root access. User-installed apps, on the other hand, are installed in a user-accessible directory.
App Manager Details: Your device’s app manager usually provides information about each installed app. Look for details like the app’s developer or source. System apps are often developed by the device manufacturer or the operating system provider. Look for names like “Google,” or your device manufacturer like “Samsung” or “OnePlus.”
Disable Option vs. Uninstall Option: In many cases, the system settings will only allow you to “disable” system apps, rather than fully uninstall them. This is a key indicator that the app is integral to system functionality. User-installed apps will usually have both a disable and uninstall option.
Pre-installation: The most obvious indicator is whether the app was present on your device from the moment you first powered it on. If it was, it’s highly likely a system app. If you installed it yourself from an app store or by sideloading, then it’s a user-installed app.
Using System Settings to Uninstall System Apps
Many Android devices allow you to uninstall some system apps directly through the system settings. This method is generally safer and easier than using ADB, as it prevents accidental removal of crucial system components. However, the availability of this option and the specific steps might vary depending on your device’s manufacturer and Android version.
Typically, the process involves navigating to the Apps or Applications section within your device’s settings. From there, select the app you wish to uninstall. If the option is available, you’ll see an “Uninstall” or “Disable” button. Disabling an app essentially renders it inactive without fully removing it from your device. This is often a safer approach than completely uninstalling, as you can re-enable the app later if necessary.
Some manufacturers may hide system apps from the default app list view. You might need to tap a menu icon (usually three vertical dots) and select “Show system apps” to see the complete list. Remember to proceed with caution. Uninstalling essential system apps can lead to instability or malfunctions.
Uninstalling System Apps Using ADB (Advanced Users)
The Android Debug Bridge (ADB) offers a more powerful method for uninstalling system apps, but it requires technical proficiency and comes with greater risks. Incorrect usage of ADB commands can severely impact your device’s stability. Proceed with extreme caution.
Before starting, ensure you have the necessary tools:
- ADB installed on your computer.
- USB debugging enabled on your Android device.
- Your device connected to your computer via USB.
To uninstall a system app using ADB, follow these steps:
- Open a command prompt or terminal on your computer.
- Enter the following command to verify your device is connected:
adb devices - Identify the package name of the system app you wish to uninstall. You can use a package name viewer app from the app store.
- Execute the uninstall command:
adb shell pm uninstall -k --user 0 <package_name>. Replace<package_name>with the actual package name of the app.
The -k flag keeps the app’s data and cache directories, while --user 0 specifies the primary user profile. Double-check the package name before executing the command, as uninstalling essential system apps can render your device unusable.
Restoring Uninstalled System Apps

Uninstalling system apps can sometimes lead to unexpected issues. Restoring these apps is often the best solution to rectify problems. The method for restoring system apps varies depending on your device and operating system. Here are a few common approaches:
Using Your Device’s Application Manager
Some devices provide a feature within the Application Manager (or similar utility) to reinstall or enable previously uninstalled system applications. Look for an option like “Disabled apps” or “Show system apps.” If the uninstalled app is listed there, you may be able to re-enable or reinstall it directly.
Factory Reset
A factory reset will restore your device to its original state, including all pre-installed system applications. This is a more drastic measure and will erase all your data, so back up important information before proceeding.
Using System Update or Recovery Image
On some devices, applying a system update provided by the manufacturer may reinstall missing or uninstalled system apps. In more advanced scenarios, using a recovery image (often downloaded from the manufacturer’s website) can help restore the device to a clean state, reinstalling all system components.
Alternative Methods for Disabling System Apps
If you’re hesitant to completely uninstall system apps, disabling them offers a less drastic approach. Disabling an app prevents it from running in the background and removes its icon from the app launcher, effectively hiding it without permanent removal. This is often a preferred method as it preserves the app’s files should you need to re-enable it later.
The process for disabling system apps is typically straightforward:
- Open your device’s Settings app.
- Navigate to the Apps or Application Manager section.
- Locate the system app you wish to disable.
- Tap on the app and select Disable.
Note: The exact steps might vary slightly depending on your device’s manufacturer and Android version. Some system apps crucial for core functionality might not offer the disable option.
Troubleshooting Issues After Uninstalling System Apps
Uninstalling system apps can sometimes lead to unexpected issues. This section provides troubleshooting steps for common problems.
Boot Loops or System Instability: If your device enters a boot loop (repeatedly restarts) or becomes unstable after uninstalling a system app, it indicates a crucial system component was removed. Try rebooting your device in safe mode. If the problem persists, a factory reset might be necessary, though this will erase all data.
App Incompatibility: Some apps rely on specific system apps for functionality. If an app starts malfunctioning after a system app removal, the removed app was likely a dependency. Reinstalling the system app is the solution.
Reduced Functionality: Certain features of your device might stop working correctly if a related system app is uninstalled. For instance, uninstalling a core system app linked to Wi-Fi might disable wireless connectivity. Identify the uninstalled app causing the issue and reinstall it.
Error Messages: Pay close attention to any error messages displayed. They often provide clues about the cause of the problem and which app is involved. Note down the error message and research potential solutions.
Recommendations Before Uninstalling Any System App
Before you uninstall any system app, it’s crucial to take precautionary steps to avoid potential problems. Uninstalling the wrong app can lead to system instability or even brick your device.
Back up your device. This is the most important step. A full backup allows you to restore your device to its previous state if anything goes wrong.
Research the app thoroughly. Understand the app’s function and its dependencies. Use a search engine to see if others have experienced issues after uninstalling the same app.
Consider disabling the app first. If possible, disable the system app instead of uninstalling it. This allows you to revert the change easily if you encounter problems. If disabling solves the issue, you may not need to uninstall it.
Use a reputable app uninstaller. If you’re using a third-party app for uninstalling system apps, ensure it’s from a trusted source and has positive reviews.